QR Code

Products
Contact Us

Fax
+86-574-87168065

E-mail

Address
Luotuo Industrial Area, Zhenhai District, Ningbo City, China
How Do Bevel Gears Differ from Other Gear Types? If you're sourcing mechanical components, you've likely encountered various gear types. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right part for your application. Bevel gears are unique in their ability to change the direction of power transmission between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. Unlike parallel shaft arrangements of spur or helical gears, or the crossed-axis complexity of worm gears, bevel gears offer a compact and efficient solution for directional changes. This makes them indispensable in countless industrial and automotive applications, from differentials in vehicles to complex machinery. Choosing the wrong gear type can lead to system failure, increased downtime, and higher costs. This guide will break down the key distinctions, helping you make an informed decision for your next project. For reliable and precise Bevel Gear solutions, consider partnering with Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited to address your specific transmission challenges.
Article Outline:
A common pain point in machinery design is transmitting power between shafts that are not parallel. Using standard spur gears here is impossible, and helical gears would create excessive axial thrust and inefficiency. This is the precise scenario where bevel gears excel. Their conical shape allows teeth to mesh smoothly on intersecting axes, providing a robust and reliable method for changing the drive direction. The solution lies in selecting the correct bevel gear type—straight, spiral, or hypoid—based on your requirements for speed, torque, noise, and efficiency.
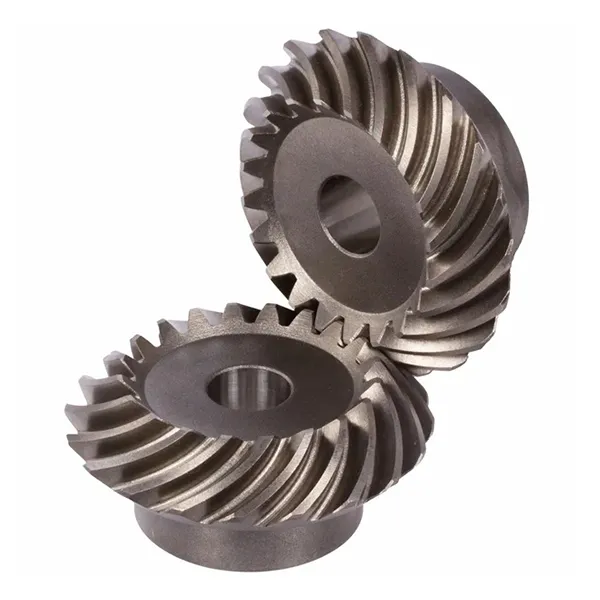

For instance, when you need a quiet operation with high load capacity for automotive differentials, spiral bevel gears from a trusted supplier like Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited are the ideal choice. Their curved teeth engage gradually, reducing vibration and noise compared to straight bevel gears.
| Parameter | Straight Bevel Gear | Spiral Bevel Gear | Hypoid Bevel Gear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Low-speed, moderate load applications | High-speed, high-load applications (e.g., vehicle differentials) | Applications requiring offset shafts for lower profile |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower | Low |
| Efficiency | Good | Excellent | Very Good |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Lower | Higher | Highest |
Engineers often face the dilemma of balancing performance with cost and manufacturability. The tooth design of a gear directly impacts this balance. Straight bevel gears have simple, straight teeth tapering towards the apex, making them easier and less expensive to produce. However, they can be noisy and are unsuitable for high-speed operations. In contrast, spiral bevel gears feature curved, oblique teeth. This design allows for multiple teeth to be in contact simultaneously, leading to smoother, quieter, and stronger power transmission capable of handling higher speeds and loads.
The solution for demanding applications is to opt for spiral or hypoid bevel gears. Hypoid gears, a special type of spiral bevel gear, have axes that do not intersect, allowing for larger pinion diameters and higher strength. This is critical in heavy-duty machinery. Partnering with an expert manufacturer ensures you get the right tooth design. Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited provides precision-engineered spiral and hypoid gears that solve problems related to noise, durability, and space constraints in complex assemblies.
| Feature | Spur Gear | Helical Gear | Bevel Gear (Spiral) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft Orientation | Parallel | Parallel | Intersecting (Typically 90°) |
| Tooth Engagement | Sudden, line contact | Gradual, line contact | Gradual, point/line contact |
| Noise & Vibration | High | Moderate | Low |
| Axial Thrust | None | Significant | Moderate |
| Best For Direction Change? | No | No | Yes |
A major sourcing headache is receiving gears that fail prematurely due to substandard materials or imprecise manufacturing. The performance and lifespan of a bevel gear are dictated by these two factors. High-carbon steel or alloy steel is commonly used for their strength and hardness, often enhanced through heat treatments like carburizing. The manufacturing process, especially for spiral and hypoid gears, requires advanced CNC machinery and strict quality control to achieve the necessary tooth profile accuracy and surface finish.
The solution is to source from a manufacturer with proven expertise in material science and precision grinding. Inaccurate gears lead to inefficiency, heat buildup, and catastrophic failure. Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited mitigates this risk by utilizing high-grade materials and state-of-the-art manufacturing processes to deliver bevel gears that meet exact specifications for toughness, wear resistance, and quiet operation, ensuring your machinery runs reliably.
| Material | Typical Application | Key Properties | Common Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (e.g., AISI 1045) | General industrial, straight bevel gears | Good strength, machinability, cost-effective | Through-hardening |
| Alloy Steel (e.g., AISI 4140, 8620) | High-load, automotive, spiral bevel gears | High strength, toughness, wear resistance | Carburizing, Case Hardening |
| Stainless Steel | Food, marine, corrosive environments | Corrosion resistance, moderate strength | Often solution treated |
Q: How Do Bevel Gears Differ from Other Gear Types in terms of maintenance?
A: Bevel gears, especially precision spiral and hypoid types, require careful alignment and specific lubrication. Unlike simple spur gears, misalignment in bevel gears causes rapid wear and noise. Maintenance involves regular checks for proper backlash, alignment of intersecting shafts, and using the correct high-pressure lubricant. Partnering with a supplier like Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited ensures you receive gears built for longevity and clear maintenance guidelines.
Q: Can Bevel Gears be used for non-90-degree shaft angles?
A: Yes. While 90 degrees is most common, bevel gears can be manufactured to operate at various intersecting shaft angles (e.g., 45°, 60°, 120°). This flexibility is a key differentiator from other gear types designed for fixed parallel shafts. The design and manufacturing complexity increases with non-standard angles, which is why working with an experienced technical partner is essential for success.
We hope this guide has clarified the unique role of bevel gears in power transmission systems. The right gear choice impacts efficiency, noise, and the total cost of ownership. Do you have a specific application or challenge involving shaft direction changes? We'd love to hear about it and discuss potential solutions.
For your precision gear requirements, consider Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited, a trusted leader in the design and manufacturing of high-quality transmission components including bevel gears. With a commitment to engineering excellence and customer satisfaction, Raydafon provides tailored solutions for industries worldwide. Visit our website at https://www.transmissions-china.com to explore our capabilities or contact our sales team directly at [email protected] for a consultation.
Litvin, F.L., 1994, Gear Geometry and Applied Theory, Prentice Hall.
Zhang, Y., et al., 2018, "Load Distribution and Transmission Error of Spiral Bevel Gears with Mismatch Tooth Surface," Journal of Mechanical Design, 140(3).
Shih, Y.P., 2010, "A Novel Ease-Off Topography Method for Spiral Bevel and Hypoid Gears," Mechanism and Machine Theory, 45(3), pp. 1108-1124.
Simon, V., 2007, "Influence of Tooth Modifications on Tooth Contact in Hypoid Gears," Mechanism and Machine Theory, 42(8), pp. 917-937.
Wang, J., et al., 2020, "Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of spiral bevel gears based on loaded tooth contact analysis," Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 12(5).
Kawasaki, K., et al., 2005, "Tooth Contact Analysis of Zerol Bevel Gears," ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences.
Fan, Q., 2006, "Computerized Modeling and Simulation of Spiral Bevel and Hypoid Gears Manufactured by Gleason Face Hobbing Process," Journal of Mechanical Design, 128(6), pp. 1315-1327.
Ding, H., et al., 2019, "A data-driven optimization model for collaborative design of spiral bevel gears in CAD-CAM-CNC chain," Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 57, pp. 140-151.
Tsai, Y.C., Hsu, W.Y., 2007, "The Study on the Design of Spiral Bevel Gear Sets with Circular-Arc Teeth," Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 192-193, pp. 266-274.
Argyris, J., et al., 2002, "Computerized Integrated Approach for Design and Stress Analysis of Spiral Bevel Gears," Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 191(11-12), pp. 1057-1095.
-



+86-574-87168065


Luotuo Industrial Area, Zhenhai District, Ningbo City, China
Copyright © Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited All Rights Reserved.
Links | Sitemap | RSS | XML | Privacy Policy |
